Quality Improvement Resources
Quality Improvement Resources – Australia and International Tools
Quality improvement is of paramount importance in healthcare organizations providing care to people living with diabetes. Quality improvement programs can help healthcare organisations ensure that patients with diabetes receive the highest quality of care possible, leading to improved outcomes and better care for people living with diabetes.
Quality improvement in healthcare organisations providing care to people living with diabetes includes several key elements. These include regular monitoring of patient outcomes, identifying areas for improvement, implementing evidence-based best practices, and measuring the impact of interventions. By continuously assessing and improving care processes, healthcare organisations can ensure excellence in diabetes care.
Effective quality improvement can also help reduce the costs and burden of diabetes by improving rates of hospital admissions, lower the incidence of diabetes-related complications such as heart disease and kidney failure, and improve patient satisfaction.
In conclusion, quality improvement is crucial for services providing care to people living with diabetes. By implementing evidence-based practices and regularly monitoring patient outcomes, healthcare centres can improve the quality of care and patient satisfaction, reduce the incidence of complications, and achieve cost savings.
The below list is some of the resources available to support healthcare services wishing to undertake quality improvement activities in Australia. Other resources may also be available at the state or territory level, or through professional associations and networks.
What resources are available to support healthcare services wishing to undertake quality improvement activities in Australia?
PRIMARY CARE RESOURCES
AUSTRALIAN COMMISSION ON SAFETY AND QUALITY IN HEALTH CARE
The Commission provides resources, tools, and guidelines to support healthcare organizations in improving the quality and safety of their services. The Commission’s website also offers access to national standards and accreditation programs, as well as reports and data on quality and safety in healthcare.
Measurement for Improvement Toolkit A : Download PDF– 841 KB (841.34 KB)
Measurement for Improvement Toolkit B: Download PDF– 682 KB (682.26 KB)
Measurement for Improvement Toolkit C: Download PDF– 2 MB (1.69 MB)
NSQHS Standards safety and quality improvement guide for governance for safety and quality in health service organisations: Download PDF – 1 MB (1.06 MB)
CLINICAL EXCELLENCE COMMISSION (CEC)
The Clinical Excellence Commission provides a range of tools and resources to support NSW Health staff to improve the quality of care for our patients. The tools and resources include graphs, charts, diagrams and mapping tools designed to help you plot the data around your intended quality improvement initiative.
By using these tools and resources throughout your Quality Improvement initiative, you and your team can gain a better understanding of the underlying problems that are causing the issue, gain insight as to how best to go about the improvement and develop an effective strategy to complete your project.
Each tool includes background information and instructions on how and when it should be used. Accompanying templates (Excel or PowerPoint) have been developed and are available for staff to download and use with their own data. Links to instructional videos have also been included for most tools, to further assist in the explanation of the resource.
NPS MEDICINEWISE QUALITY IMPROVEMENT HUB
Practical information, tools and resources for health professionals and staff in general practice to help improve the quality of health care and safety for patients.
BRISBANE SOUTH PHN AND DIABETES QUEENSLAND
The QI toolkit is made up of modules that are designed to support a primary care practice to make easy, measurable and sustainable improvements to provide best practice care for patients. The toolkit will help the practice complete QI activities using the Model For Improvement (MFI). The MFI uses the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle, a tried and tested approach to achieving successful change.
Quality Improvement Toolkit for General Pracitce – Diabetes Module (v2)
HUNTER NEW ENGLAND AND CENTRAL COAST PHN
Here you will be able to find resources and information that will assist your practice in the implementation of these strategies, alongside the development and integration of quality improvement activities for Diabetes to use in Primary Health Care.
RECORD TEMPLATES
12 Month Quality Improvement Record Template V3
Quality Improvement Record PDSA
Practical Examples
- Diabetes Cycle of Care PDSA Example
- Learn more about Diabetes Cycle of Care PDSA Example
- Quality Activity 1 Diabetes Indicated No Coded Diagnosis
- Learn more about Quality Activity 1 Diabetes Indicated No Coded Diagnosis
- Quality Activity 2 Chronic Disease Management
- Learn more about Quality Activity 2 Chronic Disease Management
- Quality Activity 3 Diabetes Register
- Learn more about Quality Activity 3 Diabetes Register
- Quality Activity 4 Diabetes Cycle of Care
- Learn more about Quality Activity 4 Diabetes Cycle of Care
Fundamentals Guide
CENTRAL QUEENSLAND, WIDE BAY, SUNSHINE COAST PHN
Their toolkit is intended as a guide for how quality improvement in general practice can be used to improve outcomes for people living with, or at risk of developing diabetes.
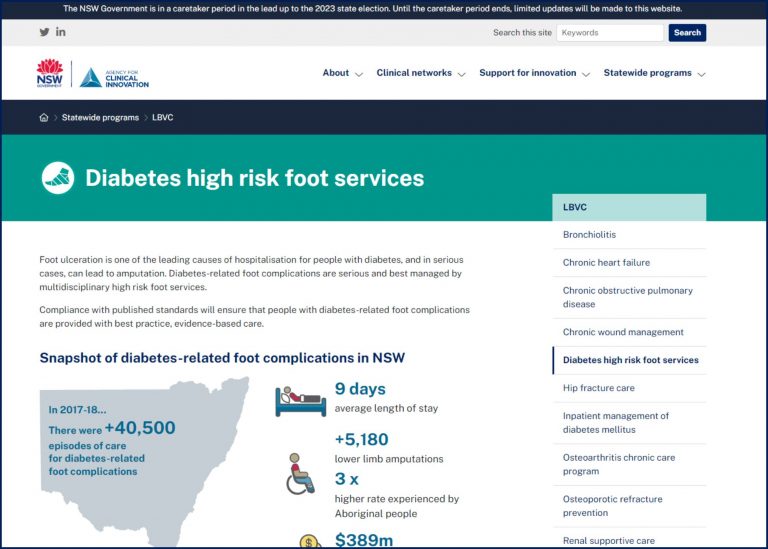
ACI – DIABETES HIGH RISK FOOT SERVICES
Foot ulceration is one of the leading causes of hospitalisation for people with diabetes, and in serious cases, can lead to amputation. Diabetes-related foot complications are serious and best managed by multidisciplinary high risk foot services.
Compliance with published standards will ensure that people with diabetes-related foot complications are provided with best practice, evidence-based care.
CLICK HERE: Diabetes High Risk Foot Services: Monitoring and evaluation plan
International Quality Improvement Tools and Resources
Institute of Healthcare Improvement (US based)
POPULAR TOOLS
- Driver Diagram
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) Tool
- Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) Worksheet
- Quality Improvement Essentials Toolkit
- SBAR Tool: Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation
POPULAR IHI WHITE PAPERS
- A Framework for Safe, Reliable, and Effective Care
- Achieving Health Equity: A Guide for Health Care Organizations
- Achieving Hospital-wide Patient Flow
- Comparing Lean and Quality Improvement
- IHI Framework for Improving Joy in Work
- IHI Global Trigger Tool for Measuring Adverse Events (Second Edition)
- The Breakthrough Series: IHI’s Collaborative Model for Achieving Breakthrough Improvement
NEWEST PUBLICATION
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US Gov Based)
Improving Diabetes Care Quality
My Quality Improvement (MyQI)
After reviewing your MONAHRQ-generated information for diabetes, you may be ready to take steps to improve the quality of care of diabetes in your area.
The MyQI Improving Diabetes Care Quality portal provides a framework, action steps, and resources for planning and implementing initiatives to improve the quality of diabetes care in the community, thereby reducing hospitalizations for diabetes patients.
The goals of improving the quality of diabetes care are to close gaps between current and best medical practice, improve access to care, and eliminate disparities.
Resources and links in this portal answer these questions:
PREMs and PROMs are also valuable tools in a Diabetes Services Quality Improvement Toolkit
Patient-Reported Experience Measures (PREMs) and Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) are two terms that are often used interchangeably but are quite distinct from each other. While they are complementary in nature, they measure different aspects of patient care and can achieve significant improvements when used together.
The importance of a patient’s perspective in providing quality healthcare is widely recognised in the medical community. PREMs ask patients about their experience of care, usually through validated survey tools that focus on the core drivers of a good patient experience. By collecting this information, healthcare providers can identify areas for improvement and create benchmarks for quality across the organization, region, or country.
On the other hand, PROMs capture the impact of illness, health condition, symptoms, or side-effects from the patient’s perspective. These measures are used to assess a patient’s health status at a particular point in time or over a period of time. PROMs are often collected before, during, and after treatment for a health condition, and they provide valuable information about the effectiveness of interventions and their impact on patient outcomes.
Research has shown that both PREMs and PROMs are essential in supporting a patient-centred approach to care, quality improvement, and organizational performance. By measuring both patient experience and outcomes, healthcare providers can gain a more complete understanding of the quality of care they are delivering and identify areas for improvement.
Capturing PROMs alongside traditional clinical outcomes can offer a range of benefits, including better communication with patients, identification of problems, and tailored care to meet individual needs. Additionally, PROMs have been shown to provide significant improvements in quality of life and survival rates in various conditions such as diabetes, cancer, stroke, orthopaedics, cardiology, rheumatology, and respiratory diseases.

In summary, PREMs and PROMs are powerful tools that healthcare providers can use to improve the quality of care they deliver. By measuring both patient experience and outcomes, providers can gain a more complete understanding of the quality of care they are delivering and identify areas for improvement. These measures are essential to supporting a patient-centred approach to care, improving healthcare delivery, and achieving better patient outcomes.
Both PREMs and PROMs tools (including those for CALD groups) are available in the NADC PERL resources. For more information about PERL, please head to: https://nadc.net.au/perl/
Value Based Healthcare
Value-based healthcare is an approach that aims to provide the best possible outcomes to patients at the lowest possible cost, utilizing all available resources and expertise. NSW Health defines value-based healthcare as the following:
Continually striving to deliver care that improves:
- health outcomes that matter to patients
- experiences of receiving care
- experiences of providing care
- effectiveness and efficiency of care.
Value based healthcare should be driven by patients, clinicians and the community
Value based healthcare requires engagement from patients, the community, clinicians and organisations. A collaborative approach will ensure that we deliver the best outcomes for patients and the best value for the system.
To achieve this, it’s crucial to consider patients as partners in their care, taking into account not only their clinical needs but also their emotional, mental, spiritual, social, and financial needs.
Digital technology plays a vital role in enabling patients to share their perspective in real-time, providing valuable insights that can be used to make a quantifiable difference.
To achieve a patient-centric and value-based healthcare system, healthcare providers must work closely with patients and utilise tools such as PREMs and PROMs. By using these tools together, providers can engage with patients more effectively, capture their experiences and outcomes, and utilize the insights gained to continually improve the quality of care.
Ultimately, this approach enables healthcare providers to deliver the best possible outcomes to patients while making the most efficient use of available resources.
Finally, don’t forget that undertaking any of the NADC Accreditation programs is an enormous quality improvement process in itself. Click on any of the below links to find out more about our accreditation for: